The Chinese Language
What is the Chinese language? Is Chinese a single language?
Join us to discover what the Chinese language really is!

An introduction to the Chinese language
The Chinese language is the world’s most widely spoken language.
The Chinese language is fascinating and unique. Unlike most other languages, the Chinese language both has a written form and several spoken forms. The main spoken form, used officially in China, is called Mandarin.
By knowing Mandarin, you’ll be able to communicate with almost anyone in China and in Taiwan. Let Ninchanese, the most effective way to learn to speak Mandarin, guide you in your learning and you’ll be ready to make 1.3 billion new friends in just a few months. Doesn’t that sound great?
Try Ninchanese for freeLet’s explore the Chinese Language
Ready for a trip from written Chinese to the different forms of Chinese spoken in China?
Written Chinese
Chinese is the oldest written language in the world, dating back to over 4000 years ago.
Traces of written Chinese were found as early as under the Shang dynasty (1600 – 1066 BC). We owe the Chinese language used nowadays in China to the Han dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD).
Unlike in other languages, there is no Chinese alphabet.
Instead, the Chinese language uses Chinese characters, which are called 汉字 hàn zì. Early characters were drawn to resemble objects. Chinese characters then evolved to come to represent ideas rather than syllables. Chinese characters have a meaning independently of the sounds you can make to describe them.

Universal Chinese characters
Written Chinese can be understood by all those who can read Chinese characters,
regardless of what spoken form of Chinese they speak. Isn’t that clever?
That’s why learning Chinese characters is important. For a fun way to discover written Chinese,
that makes you want to learn Chinese characters, give Ninchanese a try.
Spoken Chinese
Is Chinese the same as Mandarin? What Chinese should you learn? Read on for answers to your burning questions
How many spoken Chinese languages are there?
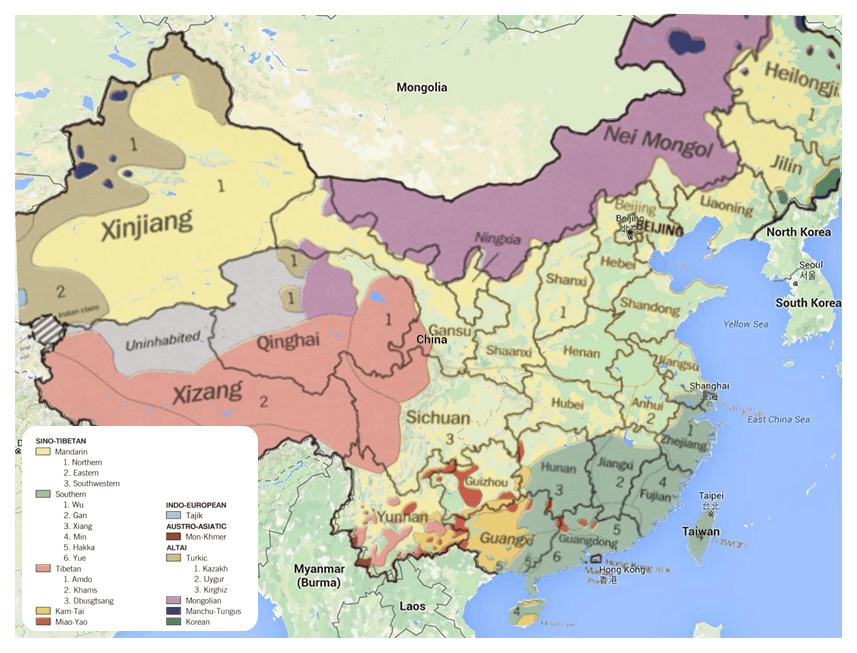
The Chinese language is actually a family of languages. See, in the Chinese language, in addition to Mandarin, there are many forms of spoken Chinese. These different Chinese languages are sometimes called dialects.
It’s considered that in China, there are more than 200 dialects. These dialects stem from the 56 ethnic minorities that Chinese is home to. Chinese speakers usually use a dialect that belongs to one of these 7 groups of languages: Mandarin, Yue (Cantonese), Xiang (Hunanese), Min, Gan, Wu, and Kejia or Hakka.
How close are these Chinese languages?
All versions of spoken Chinese are part of the same family, which is part of the Sino-Tibetan language group. They are therefore closely related. These Chinese languages share a tonal system, which is used to differentiate homonyms.
Mandarin Chinese has five tones, and other Chinese languages can have more. 粤 Yuè (Cantonese) for example has 9 tones. They also all use the same written language: Chinese characters.
However, despite being closely related, these different languages are mutually unintelligible. This is why all Chinese citizens are taught a common, official language: Mandarin.
The Chinese languages are all part of the same family: The Sino-Tibetan language group.
Despite that, they are all mutually unintelligible.
The official language in China
Mandarin is China’s official language other countries in Asia.
Mandarin is taught in schools throughout the country. The media, officials, and the government use Mandarin as their main language. When you type in Chinese, you use a phonetic system, called pinyin, that corresponds to the Mandarin pronunciation. In addition to China, Mandarin Chinese is an official language in several other countries in Asia. It is also now one of the six official languages of the United Nations.
More than 70% of the Chinese population speaks Mandarin as their first language. The remaining 30% now often learns both their regional dialects and Mandarin so they can communicate with everyone. As long as you know Mandarin, you’ll be fine anywhere.
More than 70% of China’s population speaks Mandarin as their first language.

Mandarin
Mandarin is one of the two names given by the Westerners to talk about the official Chinese language. At school, when you study Chinese, you’re actually learning Mandarin for most of the time. On Ninchanese, you learn Mandarin Chinese as well.

Standard Chinese
In the West, you can also hear the Chinese language referred to as Standard Chinese, also called Modern Standard Mandarin. When we talk about Standard Chinese, we mean the official language spoken by most of the people in China. It’s sometimes used as a synonym for Mandarin, despite not quite being the same thing. The Chinese don’t use this term a lot.

普通话 Pǔtōnghuà
普通话 literally means the “common language”. Mandarin is often its English translation. The Chinese use the term 普通话 to refer their common and official language. 普通话 is taught in school. The media, the government, and the officials all speak 普通话.

汉语 Hànyǔ
汉语 means the “language of the Han tribe”. The Han dynasty has brought a lot to the elaboration of a national language. This term is used in China to refer the Chinese language in general. It’s a bit more formal to say 汉语 than 中文 Zhōng wén which means the same thing. Chinese people living in the United States and abroad will also often say 汉语 to mention the national Chinese language.

国语 Guóyǔ
国语 Guóyǔ is another term that refers the Chinese language. 国语 literally means the “country’s language”. You’ll hear this term mainly used in Taiwan and sometimes Hong Kong to refer to Mandarin, in the same way Mainland China uses 普通话 to refer to Mandarin.

华语 Huāyǔ
Overseas Chinese communities mainly use 华语 to talk about their national and official Chinese language. 华语 literally means “China’s language”. You’ll hear Chinese communities in Singapore, Malaysia, and the Philippines use this term. 华语 is also used as a way to differentiate Chinese from the other languages spoken in these countries.
Chinese Is the New International Language
About 1.3 billion people speak the Chinese language in the world. Besides opening your mind and making you smarter, learning Chinese Mandarin will allow you to have many opportunities whether it’s a job, a cultural experience, or just the possibility of having a conversation with 1.3 billion people.
Sign upWhere can you hear Chinese spoken?
From China to the world: learn Mandarin Chinese and the world is yours
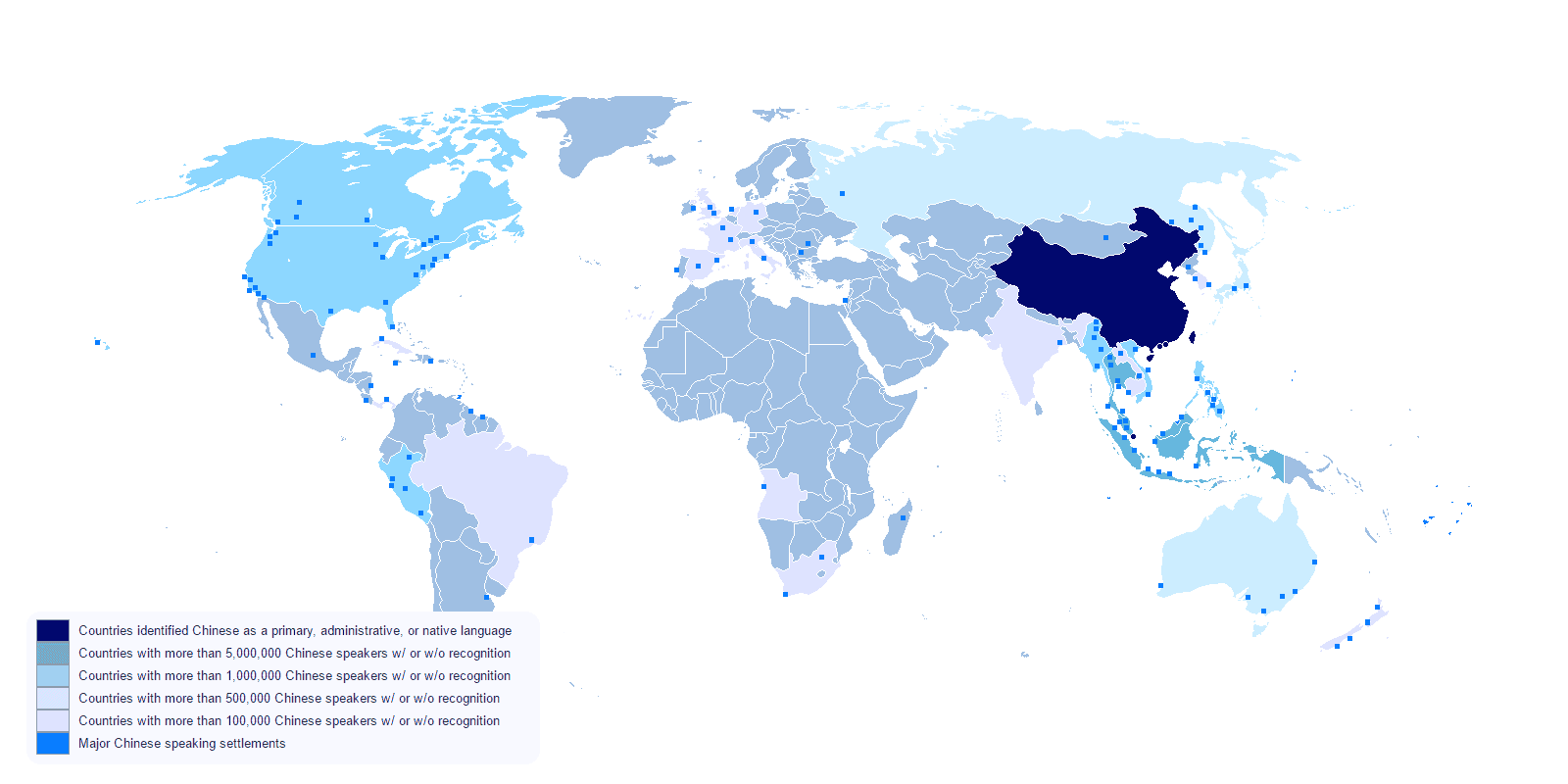
Map of the Sinophone world
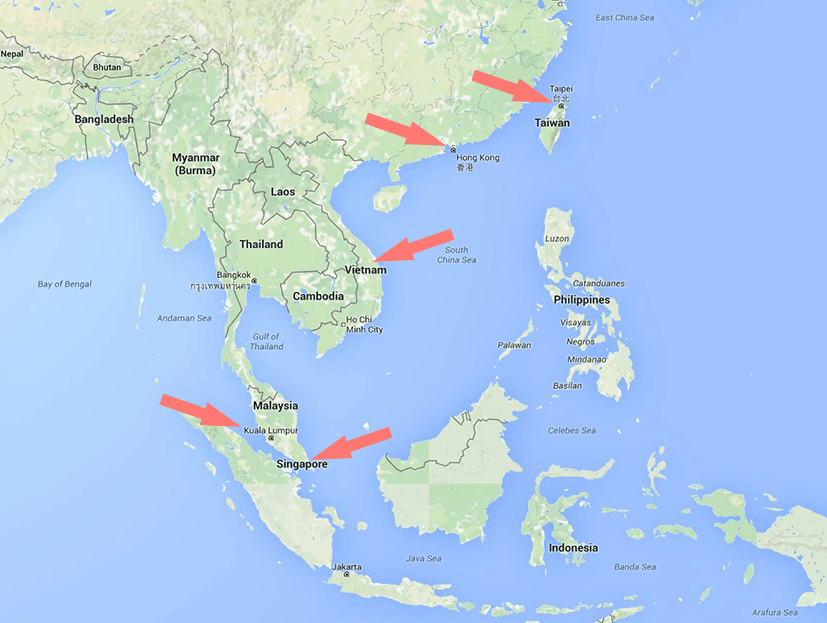
In Asia
Where you’ll find many Chinese speakers: Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore, Vietnam (Saigon) and Malaysia (especially Kuala Lumpur)
With the Chinese colonization, the Chinese language spread to Southern Asia. The Chinese wanted a harbor strategically located to control the trade with Europe and therefore conquered at one point the cities in the area that had interesting and huge harbors. Today, Mandarin Chinese is the official language in China and Taiwan, and one of the official languages in Macau and Singapore.
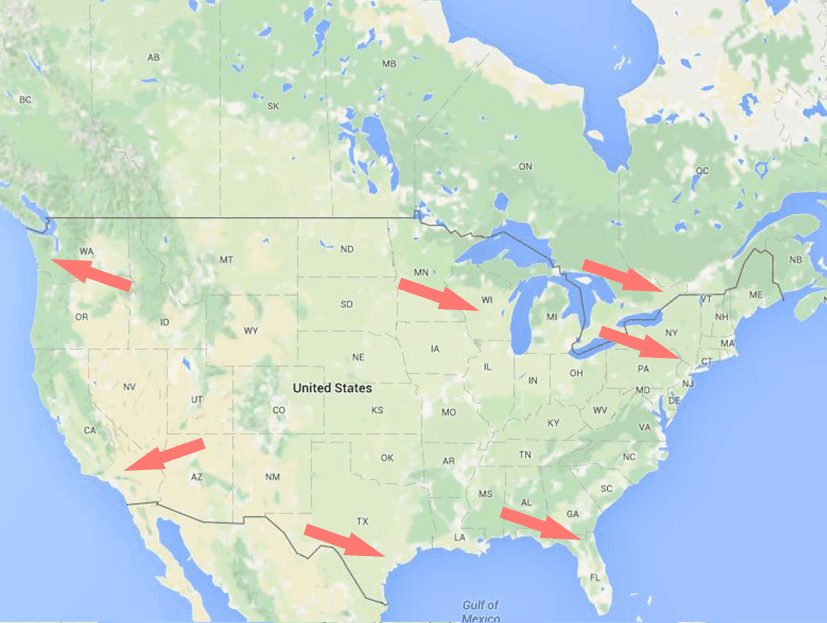
In Northern America
Where you’ll find many Chinese speakers, speaking a form of Chinese (either Mandarin or a Chinese dialect): Canada, and the US, particularly in California and in New York.
You can find many Asian and Chinese communities in Northern America. Ancient colonization is the main reason behind the fact many Chinese speakers live in North America. Immigration is another factor, especially during the Gold Rush, that makes it possible for you now to hear and practice speaking Chinese in places other than China. Many ethnic groups such as the Miao and many Cantonese people have immigrated to Canada and to the US, so you can also practice speaking other Chinese languages with them.
The Major Families of Chinese Dialects
The most commonly spoken language in China is Mandarin. But you’ll also hear many other languages in the country. Let’s take a look at these dialects and visit the different places where you can hear them.
Mandarin
China’s main dominant spoken dialect is Mandarin. Initially, people mainly spoke Mandarin, and its regional Mandarin variants in Beijing and its surroundings, as well as in Northern China. Mandarin is now China’s official language and a key to most of Asia.
Wu and Shanghainese
One of the most used dialects in China is 五华 Wǔ huá, or Wu. This group of Wu dialects includes Shanghainese, which is mainly heard in Shanghai. About 8.5% of the Chinese speaks Wu, mostly in the Zhejiang province, near Shanghai and in the neighbouring coastal areas.
Yue or Cantonese
After Mandarin, the most well-known dialect is 粤语 Yuè yǔ, Cantonese. Cantonese is particularly prevalent in South -East China: Guangzhou, Hong Kong and abroad. About 5% of the population in China uses Cantonese.
Min Chinese
Near the Fujian Province and the coastal area in the South, but also in Taiwan and in Singapore, you’ll hear lots of dialects corresponding to the 闽语 mǐn yǔ Min dialects group. The group’s most well-known dialects are probably Fuzhounese and Hokkien. You may also have heard of Hainanese and Taiwanese. About 4% of the Chinese speaks at least one Min dialects.
Hakka Chinese
People who speak dialects of the 客家话 kèjiāhuà Hakka group are scattered all over Southern China, from Sichuan to Taiwan, particularly in some parts of the Guandong and Fujian provinces. About 4% of the population can speak a dialect belonging to the Hakka group.
Gan Chinese
You may not have heard of the 赣语 Gàn yǔ, Gan dialect. Of all the main dialect groups that make up the Chinese language, this dialect is usually the dialect people know the least about. Only about 2.5% of the population speaks it. You’ll hear the Gan dialect mainly in the Jiangxi province and in some parts of the Hubei, Fujian and Hunan provinces.
Xiang
Also known as Hunanese, you’ll find the 湘语 xiāngyǔ group of dialects spoken in Hunan and in some parts of the Sichuan province as well. About 5% of the Chinese living in China speak a form of Xiang.
So what Chinese language should you learn?
If your goal is to be able to communicate with the largest number of Chinese speakers, then, without a doubt, you should learn Mandarin. Mandarin is your door to all of China, Taiwan, Singapore and many countries in Asia.
Hands-down, the best way to learn Mandarin Chinese online is Ninchanese. Get started today!
Sign up for free